Experiencing sudden lower back pain can be both alarming and distressing. Whether you were going about your day or just woke up with this unexpected discomfort, understanding the potential causes and how to address them is essential. In this article, we’ll explore the reasons behind sudden lower back pain and provide some guidance on how to alleviate it.
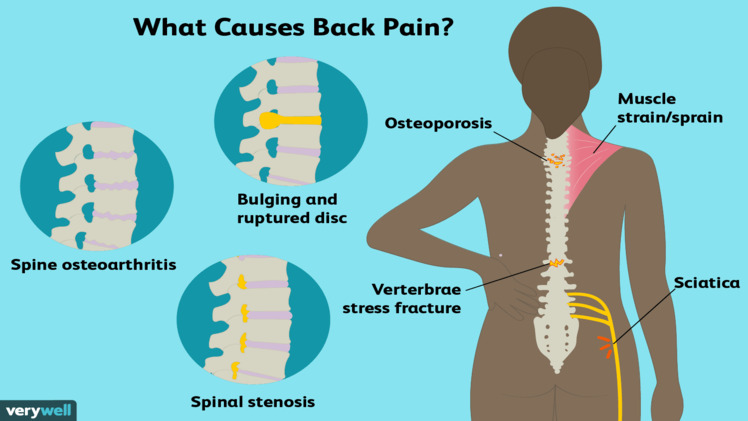
Muscle Strain: One of the most common causes of sudden lower back pain is muscle strain or sprain. This can happen due to lifting a heavy object improperly, twisting your back awkwardly, or making sudden movements that stress the muscles. The pain is often sharp and may be accompanied by muscle spasms.
Treatment: Rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain relievers can help relieve muscle strain-related pain. Gentle stretching and physical therapy may also be beneficial.
Poor Posture: Prolonged periods of poor posture, such as sitting at a desk for hours with improper ergonomics, can lead to sudden back pain. Over time, this places strain on the lower back, and it may eventually manifest as acute pain.
Treatment: Correcting your posture, using an ergonomic chair or workstation, and doing posture-improving exercises can help alleviate this type of pain.
Herniated Disc: A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner material of a spinal disc pushes through the outer shell, putting pressure on nearby nerves. This condition can cause sudden and severe lower back pain, often radiating down one leg (sciatica).
Treatment: Rest, physical therapy, and pain management techniques can help with a herniated disc. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Degenerative Disc Disease: Over time, the discs in your spine can naturally degenerate, causing discomfort and sudden pain. This condition may result from aging, genetics, or wear and tear.
Treatment: Treatment may include physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and pain management. In some cases, surgery might be recommended.
Kidney Stones: While kidney stones primarily affect the urinary system, they can also lead to lower back pain when they move through the urinary tract. The pain is usually intense, often described as excruciating.
Treatment: Treatment for kidney stones may involve medications to manage the pain and encourage the passage of stones. Larger stones may require more invasive procedures or surgery.
Infections: Infections, such as kidney or urinary tract infections, can cause lower back pain as a symptom. The pain is typically accompanied by other signs of infection, like fever and urinary symptoms.
Treatment: Antibiotics are usually prescribed to treat infections. Addressing the underlying infection will alleviate the associated lower back pain.
Arthritis: Arthritis, especially osteoarthritis, can affect the spine and cause sudden lower back pain. Arthritic conditions lead to joint inflammation, stiffness, and discomfort.
Treatment: Management of arthritis-related lower back pain may involve physical therapy, pain relievers, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, surgical procedures.
Nerve Compression: When a nerve in the lower back becomes compressed, it can cause sudden and severe pain. This compression can result from various conditions, including spinal stenosis and spondylolisthesis.
Treatment: Treatment depends on the specific cause but may involve physical therapy, medication, or surgery to relieve nerve compression.
Trauma: A sudden impact or accident, such as a fall or a car crash, can cause immediate lower back pain. In these cases, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
Treatment: Treatment varies depending on the extent of the trauma and the injuries sustained. It may involve rest, pain management, or surgical intervention.
In conclusion
Sudden lower back pain can have various causes, ranging from muscle strain to more complex conditions like herniated discs or infections. Identifying the cause of your pain is essential for appropriate treatment. If you experience persistent or severe lower back pain, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. In many cases, prompt attention and the right interventions can help alleviate your pain and get you back to your regular activities.